Evaluation of two hERG channel trafficking modulators, pentamidineand pilsicainide, on stably transfected cell line and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes
hERG trafficking inhibition is known to be one of the mechanisms of indirect hERG inhibition, resulting in QT prolongation and lethal arrhythmia. An increasing number of drugs have been shown to interfere with hERG trafficking. Pilsicainide is a widely used antiarrhythmic agent (class Ic) especially for treating atrial fibrillation. This compound has been evaluated on hERG channel current expressed in stably transfected mammalian cell line as well as on human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CM) and compared to pentamidine, a well-known hERG trafficking inhibitor.
Method
Ion channel data
Preclinical hERG assays aim to identify potential inhibitory effects early in drug discovery. Current ICH Guidelines state that hERG assays are mandatory, as a number of clinically successful drugs have had the tendency to inhibit hERG and create a concomitant risk of sudden death. As a result, a large number of drugs have been withdrawn from the market or during late stage clinical trials due to cardiotoxic effects.
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem cells derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CM)
Inhibition of the hERG channel by pharmaceutical substances is the primary cause of drug-induced QT prolongation. IKr current inhibition has been shown to prolong the cardiac action potential duration, a phenomenon associated with increased risk of QT interval prolongation. This can lead to potentially fatal ventricular tachyarrhythmia, known as Torsades de pointe.
Results
Ion channel experiments
Ion channel panel, acute exposition:
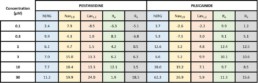
hERG channel
- No acute effect of pentamidine on hERG, Nav1.5, Cav1.2, Iks and Ito.
- Chronic exposition to pentamidine decrease the amplitude of hERG current (estimated IC50 = 9.0µM)
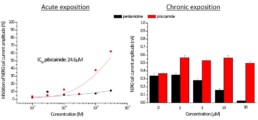
- Acute effect of pilsicainide on hERG channel (estimated IC50 = 24.6µM) but no acute effects on Nav1.5, Cav1.2, Iks and Ito.
- Chronic exposition to pilsicainide increase the amplitude of hERG current (≈+50%) whatever the concentration tested.
Ion channel panel, acute exposition:
iPSCs cardiomyocytes

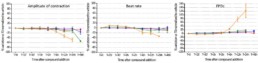
Pentamidine
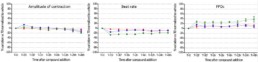
Pilsicainide
- No acute effect of pentamidine on each parameter during the first 2 hours. From 6h to 24h, pentamidine 30 μ M time-dependently ↘ amplitude of contraction, BR and CIand ↗FPDc (+123% at 24h) and BRI (at12h). After 48h, the cells stopped beating with pentamidine 30μM.
- Acute effects of pilsicainide conduct to a concentration-dependent and an ↗ of FPDc (+28% at 10µM) with maximum effect after 15 min and sustained through 48h. Pilsicainide from 1 to 10µM had no effect on amplitude of contraction and CI. The cells stopped beating immediately after pilsicainide 20µM addition.
conclusion
- Absence of pentamidine’s acute effects on hERG current in CHO cells is confirmed in Human iPSC-CM. Indeed, no modification of FPDc was observed before 6h of treatment at the highest concentration tested (30 µM).
- On the other hand, the increase of hERG trafficking observed on CHO cells by pilsicainide was not confirmed in iPSC-CM as FPDc was prolonged after short-term exposition and maintained during time.
- This predictive and sensitive assay is particularly relevant for long-term cardiotoxicity assessment in Human iPSC derived cardiomyocytes.
Please fill out the form below to receive the poster